



Get new exclusive access to healthcare business reports & breaking news




Global big data in the healthcare market is expected to reach $34.27 billion by 2023 at a CAGR of 22.07%. Globally, the big data analytics segment is expected to be worth more than $68.03 billion by 2024, driven largely by continued North American investments in electronic health records, practice management tools, and workforce management solutions.
But what exactly is big data and how can it help the healthcare industry?
This article will explain everything there is to know about big data and help you understand how it is affecting the healthcare industry.
We will:
“Big data is a term that describes the large volume of data – both structured and unstructured – that inundates a business on a day-to-day basis. But it’s not the amount of data that’s important. It’s what organizations do with the data that matters. Big data can be analyzed for insights that lead to better decisions and strategic business moves.”
The insights gained from big data can allow businesses to solve problems that could not be tackled with traditional software or analytics. In healthcare, these new insights can help researchers gain a deeper understanding of data in order to improve the results of clinical trials, boost the productivity of healthcare professionals and improve revenues of the practices themselves.


Although the term ‘Big Data’ was initially coined by Roger Mougalas in 2005, its existence can be traced back much further.
The principles of big data began with John Graunt in 1663. He analyzed the mortality rate in London and recorded the information in order to raise awareness of the effects of the bubonic plague. The statistics and analysis were published in his book Natural and Political Observations Made upon the Bills of Mortality.
This book is regarded as the first piece of recorded statistical analysis.
The principles of big data developed over the next 200 years. In 1889, the first computing system was invented by Herman Hollerith to organize census data. Fast-forward another 50 years and in 1937, passage of the Social Security Act in the United States included provisions to keep track of certain trends among American workers.
In 1943, British scientists created Colossus, the very first data-processing machine, to decipher Nazi codes in World War II. Colossus processed five thousand characters per second, reducing work that would have taken humans weeks to complete to just a few hours.
The United States built a data centre in 1965 to store tax returns and fingerprint sets. This is widely accepted as the starting point of electronic big storage.
Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web in 1989, enabled the sharing of data through a hypertext system. From here, the speed with which data could be generated rapidly increased.
This brings us to the 21st century. Enter Roger Mougalas.
This is when the term big data was first introduced to the language by Roger Mougalas. In the same year (2005), Hadoop was founded. The intention was to use Hadoop to index the entire World Wide Web. At the time of this writing, millions of businesses use Hadoop to go through vast amounts of data.
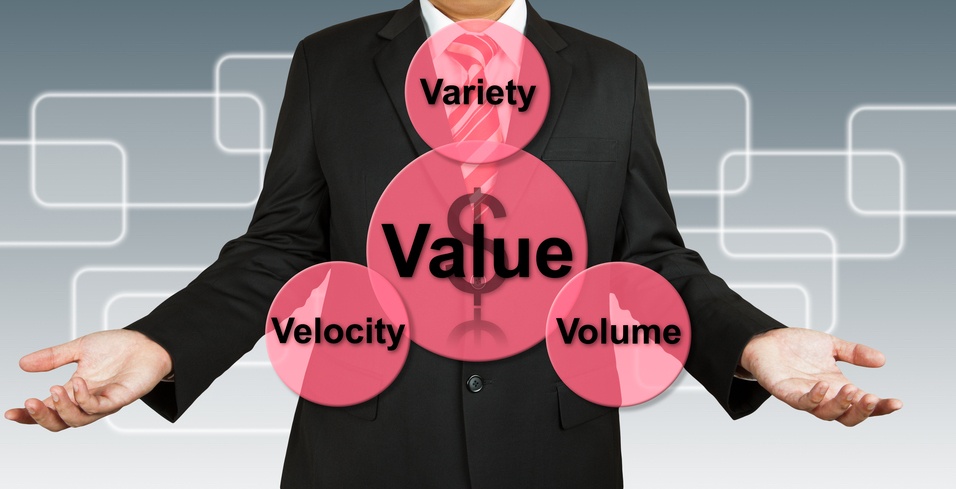

Big data relies on three Vs:
This is the amount of data generated, such as through mobile apps, websites, portals and online applications. Only 20 years ago, computers carried about ten gigabytes of memory. Today, Facebook, the largest social media platform in the world, generates 4 petabytes of new data every day. With the creation of smartphones and tablets, ever more data is being created, shared and stored across a seemingly infinitely expanding number and type of genres.
Velocity is how fast data is generated. Sticking with the theme of social media, more than 900 million photos are uploaded to Facebook every day and 500 million tweets are posted on Twitter. Big data controls this massive influx of data by accepting the incoming flow and processing it quickly to prevent any bottlenecks.
This is the generation of both ‘structured data’ and ‘unstructured data’. Variety is about being able to translate data into specific categories. Examples of structured data include texts, pictures, videos and tweets. Unstructured data examples include hand-written text, voicemail and audio recordings.


Whether it is for healthcare startups or established corporations, here are some examples of how healthcare can use big data.
Discovering and developing new drugs and other health-related products takes an amazing amount of time and money.
Big data can help reduce the time involved in a number of different ways. This, of course, serves to reduce the costs involved.
For example, during the typical research and development phase of product development, it is not always clear how to use all the data discovered. With big data techniques, R&D teams are able to find useful data much faster and more efficiently, therefore reducing the time needed to develop the product and get it to market.
Product development involves lengthy trial and error experimenting, which requires much time. Big data removes the guesswork allowing research and development companies to get results more quickly and thus develop more precise products faster.
Big data improves patient outcomes because it helps doctors and other medical professionals be more efficient and accurate with their diagnoses and treatments. With the improved data analyzing methods big data provides, doctors can hope to find solutions to treat rare and serious conditions that would otherwise seem incurable because research can progress at a faster pace.
The collection of workforce data means healthcare organizations such as hospitals and pharma companies can improve the employee output. For example, managers can redesign workflows to be more efficient and redirect resources to where they are most needed.
This is perhaps one of the largest uses of big data in healthcare. Without innovation, there would be no advancements in medicine at all. Big data will speed the rate at which new drugs can be discovered and the quality of care is improved.
These are just a few of the areas where big data can be used in healthcare. However, one of the most important uses for big data is to reduce the overall cost of healthcare. Research conducted by McKinsey & Company showed that big data could save Americans between $300 billion to $450 billion year.
In fact, by using big data and data analytics, Parkland Hospital in Dallas, Texas has reduced 30-day readmissions to Parkland and all area hospitals for Medicare patients with heart failure by 31%, for a savings of $500,000 a year. By avoiding readmission, patients also save considerable money.
The goal of efficiently using big data is to understand what is going on, identifying problems, and finding innovative solutions to them that will help reduce costs. This benefits multiple participants in medical processes such as healthcare providers, manufacturers, insurers, and, most importantly. recipients/patients.


A Dimensional Insight study found that 56% of hospitals and medical practices do not have appropriate big data governance or long-term analytics plans.
Without proper data governance, organizations run the risk of creating duplicate medical records, missing entitled reimbursements, finding difficulties for financial benchmarking and other operational inefficiencies. Big data can help with all these things!
Without analytics, patient care is also more difficult. Healthcare organizations report seeing discrepancies between clinical and accounting departments due to data mismatches and errors.
The existence of these issues is backed up by the study: 71% of the people surveyed said they have found inconsistencies in data from different sources within their organization. The most notable sectors are the financial, clinical and administrative datasets.
According to the Society of Actuaries (SOA), healthcare payers use the predictive big data analytics to pinpoint high-cost patients. They look at various patient details such as age, gender and spending history. These factors and more help to determine whether a patient should be considered high-cost.
The Healthcare Cost Institute Database reported that 17% of patients are responsible for nearly 75% of all health care expenditures. Therefore, it is important to know which patients spend more on healthcare so practitioners can provide preventive measures.
Some work on big data analytics has already begun, but there is still a far way to go to gain the most efficiency and the greatest cost reductions.
Most, if not all, healthcare sectors stand to benefit from the implementation of big data analytics. Here are a few of the big winners:
The insights generated from big data analytics enables healthcare providers, such as clinics and hospitals, to improve patient care. For example, the workflow process will improve dramatically, giving doctors more time with their patients.
Insurance providers will benefit greatly from big data in healthcare. For example, they can use it to reduce fraudulent activity, rectify false claims, provide better service to their customers and reconcile records faster. Health systems cost an average of $96 per record to manage. Anything that can help to reduce that cost will consequently improve profits.
Patients will benefit from big data in healthcare more than anyone else. They can enjoy better overall care, live healthier lives, save money on insurance and so much more.
Big data analytics will enable device manufacturers to create better, innovative products to solve health issues. They will benefit from devices relevant to their needs.
A 2013 study, published by Nature Review Drug Discovery, found that only 10% of medicines in development ever reach patients. With this in mind, big data in pharma will benefit from better research and development, resulting in more effective drugs and shorter production times. Pharma companies will also save on the costs related to drug development because the process for determining which drugs are worthwhile to enter clinical trials will be more accurate.


Whether through the use of AI in pharma or using analytics to cure cancer, there are many ways that big data could improve the industry for payers, patients and more.
Here are some of the highlights.
This is particularly useful for healthcare managers in charge of shift work. Having too many employees working on any given day runs the risk of spending too much on labor. On the other hand, not enough staff can result in poor customer service. For the healthcare industry, not enough professionals on hand can lead to fatal circumstances.
Big data analytics can overcome these problems. In fact, it is being used right now in hospitals in Paris. This article describes how Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris hospitals are using data from a variety of sources to predict how many patients are expected to be at each hospital.
The result:
“A web browser-based interface designed to be used by doctors, nurses and hospital administration staff – untrained in data science – to forecast visit and admission rates for the next 15 days. Extra staff can be drafted in when high numbers of visitors are expected, leading to reduced waiting times for patients and better quality of care.”
Smart devices and mobile apps enable patients to track their own medical information. For example, they can track the number of steps they take over the course of the day or keep an eye on their heart rate during a workout.
This health data is then stored in the cloud where doctors can analyze it and keep an eye on their patients. This means that patients don’t need to visit the medical practice for unnecessary checkups.
This information can be used to identify potential health risks that may not be easily detectable. Furthermore, when patients take more control over their health, they can be encouraged by payers and other organizations to live a healthier lifestyle. For example, companies can provide cash incentives to patients for wearing a smartwatch or fitness tracker.
Insights from big data analytics can provide key strategic planning in terms of analyzing check-up results among people in different demographic groups, identifying why they may not want a particular treatment.
For example, the University of Florida used Google Maps and free public health data to tackle issues such as chronic diseases. After comparing this data with the availability of medical services in the most heated areas, they could add more care units to the areas suffering the most.
Every patient in the US has an electronic health record (EHR) that includes medical history, allergies, demographics etc. The EHR is the most used application of big data in healthcare.
Each record can be modified by doctors across the country, meaning no paperwork is required to record a change in medical history. This improves efficiency and avoids the creation of duplicate records.
94% of hospitals in the US use EHRs. Unfortunately, other nations are not up to this standard. In the EU for example, an electronic European health record system is planned for 2020.
According to this report on big data healthcare:
“EHR that has improved the management of disease among cardiovascular disease patients, as well as yielding Kaiser Permanente an approximate savings of $1 billion…”


Considering how much data is contained in an EHR, without appropriate protection, records are prone to attacks.
There is evidence to suggest that the healthcare industry is far more likely to experience a data breach when compared to any other. In fact, research suggests that it’s 200% more likely. This is because health records contain a large quantity of personal information. In the hands of a hacker, it is incredibly valuable.
With this in mind, big data can be used to enhance cybersecurity and prevent data breaches.
Measures such as encryption technology, blockchain, firewalls and anti-virus software provide layers of protection, bringing a host of benefits.
There is another advantage here too; big data analytics can be used to prevent fraud. By systematically analyzing claims, patients can get more reliable results from their claims and get paid faster.
The potential of predictive analytics in healthcare extends beyond standard business applications. A US research collaborative (namely Optum Labs) has collected 30 million EHRs in order to improve the delivery of care.
The overall objective of healthcare business intelligence is to give doctors the ability to make quick data-driven decisions. In the case of patients who suffer from complex, rare illnesses, this ability becomes very useful.


Telemedicine is not a new concept. However, with advancements in technology, patients can connect with their doctors in ways that are much more productive. For example, they can attend virtual calls and video conferences through their smartphones and both parties can track progress with wearable tech.
Telemedicine is mostly used for initial diagnosis and remote patient monitoring. It can also be used for more advanced medical procedures, such as telesurgery – a technique where doctors perform surgeries using robots and real-time data without having to actually be in the room.
Doctors recommend the use of telemedicine to patients for personalized treatment solutions and to prevent readmissions. Healthcare big data analytics can then be linked to a predictive analytics program to predict medical events and improve the overall quality of patient care.
By reducing admissions to hospitals, telemedicine consequently reduces the cost of care – both for the patient and the medical practice itself. Patients avoid long waiting times and doctors don’t have to waste their own time on unnecessary appointments. Since telemedicine is highly accessible, doctors can monitor patient activity from anywhere and at any time.
This follows from the previous point. It is important for healthcare professionals and practices to manage their time and resources as efficiently as possible.
Kaiser Health News:reported that in Oakland, California, a woman who suffers from mental illness and substance abuse visited multiple local hospitals almost every day. It was hard for this woman to get the care she needed because her medical records were not shared among the practices, increasing costs to taxpayers and the hospitals themselves.
“Everybody meant well. But she was being referred to three different substance abuse clinics and two different mental health clinics, and she had two case management workers both working on housing. It was not only bad for the patient, it was also a waste of precious resources for both hospitals.”
So, to avoid these scenarios in the future, Alameda county hospitals created the PreManage ED program – an initiative that shares patient records between emergency departments.
This system provides workers with a host of useful data, such as whether a patient has had certain tests at other hospitals, what the results of those tests are and the advice given to the patient.
From this, it is clear that the application of big data analytics is needed. Before PreManage ED, hospitals would be required to repeat tests on a patient. Even if it was possible to see the results of the tests, it would be necessary to fax them to the other institution in order to get the required information.
Imaging procedures so so important to a large number of people. However, storing these images is costly, not to mention the time and costs involved to analyze them.
Carestream, a medical imaging provider, shows how big data analytics can change the way images are read. They explain how algorithms can analyze vast numbers of images to identify patterns in the pixels. These patterns are then converted into a number to help physicians with the diagnosis.
With this knowledge, it could be possible that, in the future, radiologists will no longer need to look at the images. Instead, all they will need to do is analyze the outcomes of the algorithms. This could change the role of radiologists and their skillsets in the medical community.


This is a very specific benefit but the outcome has the potential to help millions of people.
Data collected from patients on different treatment plans can be analyzed for trends and patterns to find those with the highest rates of success. For example, tumor samples can be analyzed to see how their mutations and proteins react to different treatments, leading to better outcomes.
A few hurdles must be overcome to make this happen, such as making data systems interfacing abilities compatible with each other, overcoming confidentiality issues (particularly in the US where states have their own laws over the sharing of personal information) and putting time and money into a dataset that institutions may not want to share with each other, even if it would more quickly lead to finding a cure.
As described by this Fast Company article, there are precedents that deal with these problems:
“The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) has hooked up with a half-dozen hospitals and universities to form the Undiagnosed Disease Network, which pools data on super-rare conditions (like those with just a half-dozen sufferers), for which every patient record is a treasure to researchers.”
Hopefully in the future, these roadblocks can be overcome and accelerate the progress being made towards curing cancer through the use of data analytics.


There are many challenges these practices face by not having big data analytics.
First, inadequate governance leads to duplicate records, missing entitled reimbursements, difficulties in financial benchmarking and other operational inefficiencies.
Patient care is also more complex these days. Without proper analytics, it becomes increasingly difficult to provide quality and safe patient care that have much better outcomes.
Finally, many healthcare organizations have seen discrepancies between clinical and accounting departments due to data mismatches.
Even with big data in healthcare, there are still challenges to face:
So how can these challenges be overcome?
Insights gained from big data can allow healthcare businesses to solve problems that could not previously be tackled with traditional software or analytics. These new insights can help gain a deeper understanding of data to improve the results of clinical trials, boost the productivity of healthcare professionals and improve revenues of the practices themselves.
Big data can help in development by reducing the time needed to develop a product and get it to market. It can also keep the costs of security down, improve patient outcomes and drive innovation.
In the modern world, every healthcare organization should be using big data. Otherwise, they run the risk of creating duplicate medical records, missing entitled reimbursements, difficulties for financial benchmarking and other operational inefficiencies. Big data can help with all these things!
Without analytics, patient care becomes more difficult too. Healthcare organizations report seeing discrepancies between clinical and accounting departments due to data mismatches and inaccuracies.
The insights generated from big data analytics enable healthcare providers, such as clinics and hospitals, to improve patient care. Insurance providers will also benefit because they can reduce fraud and more easily rectify false claims. Patients also stand to benefit because they will get better care from more efficient processes and the production of innovative products.
Many challenges come with big data in healthcare. For instance, It is important to capture relevant data from the right sources and using cloud solutions to keep the data safe and secure.
It is also important to know how to analyze this data. After all, if no one can understand what to do with it, one might just as well not have the data at all.
There are ways to overcome these challenges, such as having a data-driven mindset and using smart algorithms to produce the intended results.
Overall, though, it seems clear that everyone in healthcare benefits from big data analytics.