



Get new exclusive access to healthcare business reports & breaking news




Astaxanthin is one of the most sought-after antioxidant supplements right now – and with good reason. It’s not only an antioxidant powerhouse but also jam-packed with anti-fatigue and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as an array of other health benefits.
Part of a group of micronutrients called carotenoids, astaxanthin has a characteristic reddish color. Early research has shown that astaxanthin can help speed up the treatment of complex ailments like Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease.
That’s not all there’s to this powerful antioxidant. There are myriads of notable health benefits that come with consuming foods rich in astaxanthin.
In fact, the health effects of astaxanthin have been well documented in more than 1000 peer-reviewed medical publications and journals.
This guide is all about astaxanthin – a trend that has become an overnight sensation with multiple companies listing products that include this ingredient on popular marketplaces such as Amazon, eBay or Alibaba.
What you’ll learn from this comprehensive guide:
Let’s get right to it.
History of Carotenoids
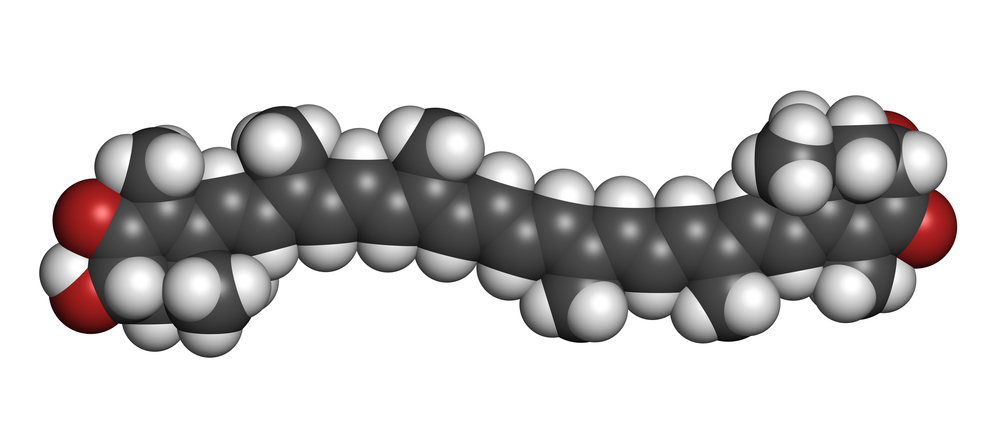

Carotenoids are pigmented phytochemicals found aplenty in plants, bacteria, algae, and a plethora of other living organisms. They are one of the most diverse groups of natural pigments, which are responsible for the bright orange, red and yellow colors primarily in veggies, fruits, and many plant parts.
Carotenoids fall under the class of fat-soluble terpenes, compounds also known as a tetraterpenoid. They are among the earliest and the most investigated phytochemicals in the history of biology. In fact, their use cases and benefits have been studied at great length dating as far back as the 1800s.
Perhaps the most recognizable member of the group is carotene, which is often associated with carrots – and, by that token, vitamin A.
Not so surprising is that carotene was the first known carotenoid. Heinrich Wilhelm Ferdinand Wackenroder actually discovered it by accident in the late 1820s while investigating a different phytochemical called anthelmintic.
It was a famous Austrian chemist Adolf Lieben, however, who is credited for discovering carotenoids in the human tissue while conducting research in 1863 at the University of Palermo.
Today, there are over 1,100 documented carotenoid compounds. They can all be placed into two broad categories:
1) Xanthophylls – These are oxygen-containing carotenoids and usually have a yellow pigment. Astaxanthin, beta-cryptoxanthin, lutein, and zeaxanthin are good examples. Foods rich in xanthophylls include pumpkin, egg yolks, avocado, summer squash, spinach, and kale. They are often linked to eye health.
2) Carotenes – These are non-oxygenated carotenoids and typically linked to orange pigment. These include alpha (α) carotene, beta (β) carotene and lycopene. Foods rich in carotene include papaya, tomatoes, tangerines, sweet potatoes, cantaloupe and, of course, carrots.
No matter the category, all carotenoids boast antioxidant properties which varies depending on the actual compound. From a historical standpoint, they are almost synonymous with vitamin A.
That in and of itself isn’t surprising because some carotenoids are converted into vitamin A when ingested into the body. These include beta-cryptoxanthin, beta carotene, and alpha-carotene. Others like lycopene, zeaxanthin, and lutein don’t convert to vitamin A.
Astaxanthin is an increasingly popular carotenoid which belongs to the subclass of xanthophyll. It occurs naturally in certain algae and runs the color gamut from red to pink. Some astaxanthin can also be found in specific seafood types.
In fact, it is what causes the reddish color in lobster, salmon, fish eggs, trout, crabs, and other seafood. This substance is also what is responsible for the pinkish color in the features of flamingo.
In everyday and technical use, astaxanthin goes by many other names, including 3R,3’S-astaxanthin, 3R,3’R-astaxanthin, 3S,3’S-astaxanthin, 3,3′-dihydroxy-4,4′-diketo-beta-carotene, Dihydroxy-3,3′ dioxo-4,4′ bêta-carotène, Ovoester, Micro-Algue, Microalgue, Microalgae, Astaxantina or Astaxanthine.
Astaxanthin is often referred to as ‘the king of carotenoids’ because of its reputation as one of the most powerful antioxidants found in nature.
The substance is of particular significance because it never converts to become a pro-oxidant. This means that it can never bring destructive oxidation in the body, making it perfect for health-related benefits and performance.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today.
That being said, astaxanthin as an antioxidant helps reduce oxidation, a natural that is responsible for the vast majority of inflammation cases in our bodies. If not reduced, prolonged inflammation can cause insurmountable damage to our health and well-being.
Specifically, inflammation is responsible for early aging, brain-related conditions like dementia, eye problems, heart disease, arthritis, and an array of cancers. By the virtue of being an effective antioxidant, astaxanthin can help with these conditions and a long list of other health complications.


Your body cannot produce astaxanthin on its own, which means you have to get it through food or dietary supplements. Those who prefer astaxanthin-rich foods should consume plenty of salmon, shrimp, lobster, rainbow trout, and other seafood.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today.
Seafood, however, might not be a plausible way to get significant amount of astaxanthin. The richest seafood source – sockeye salmon, for instance, has only 4.5mg of the compound per every ounce. That’s not enough to spur the desired health benefits.
That’s why most people go for dietary supplements. Those based on Pluvialis algae have the highest bioavailable amount of astaxanthin. 3 percent of its biomass is pure astaxanthin. In fact, it is the only supplement has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a safe and viable source of dietary astaxanthin.
Phaffia rhodozyma, a popular red yeast, and some crustacean are the other two main commercially viable sources of astaxanthin. There exists also synthetic astaxanthin that has been traditionally used by manufacturers to produce food coloring and fish feed.
So, how does astaxanthin actually work? It’s pretty simple and straightforward: it’s an antioxidant.
Get this:
Against this background, it is quite clear that astaxanthin is hands down one of the best ways to ingest antioxidants into your body.
As you may already know, antioxidants are important for your body. They play a big role in human growth, health, and wellness. These nifty compounds boast some of the most powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
Antioxidant properties of astaxanthin help explain its health benefits and claims, particularly when used to help manage and treat a variety of diseases like cancer.
Biologically speaking, antioxidants are agile molecules that repair damage caused at the cellular level by unstable, harmful molecules called free radicals. These molecules are constantly being released during metabolism.
Don’t get it wrong; free radicals are there to serve a purpose too. For instance, our disease-fighting immune system uses certain free radicals to kill viruses, bacteria and other germs that try to infect our bodies.
Unfortunately, untamed free radicals can also destroy good cells. There’s supposed to be a subtle balance between free radicals and antioxidants. In fact, it is the job of antioxidants like astaxanthin to keep free radicals in check.
Anything that stifles this balance can lead to oxidative stress, a state which could be detrimental to our body. Antioxidants act on free radicals by donating electrons to them. This process renders free radicals stable and neutralized.
So, by definition, antioxidants reverse the process oxidation – and therefore prevents oxidative stress from occurring. Persistent oxidative stress can lead to increased risk of bad health outcomes, including neurodegenerative disorders, heart disease, and a number of cancers. Prolonged interference by free radicals can contribute to accelerating the aging process.
In our everyday lives we are exposed to several risk factors that increase the formation of free radicals. Some lifestyle habits and environmental factors that encourage oxidative stress.
They include excessive alcohol intake, high carb diet, certain toxins, cigarette smoking, excess consumption of certain metals (zinc, copper, magnesium, or iron), too much or too little oxygen in the blood, air pollution, and infections, just to mention a few.
As we have mentioned earlier, the number of studies that have been conducted on the effectiveness and health benefits of astaxanthin reach in the thousands. Let’s take a look at some of the most important health benefits:
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today.


Today, over 30 million people in the US have diabetes, and a huge chunk of that die every year. In fact, diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the country. Overweight and obese people are at the highest risk of diabetes.
Diabetes is caused by problems with the insulin-producing pancreas. More specifically, this happens when pancreatic beta cells are damaged, inflamed or otherwise malfunctioning. When these cells are destroyed, the pancreas produces very little or no insulin at all.
Insulin is a useful hormone that plays a key role in regulating how sugar and fats you consume are used or stored in your body.
It so happens that oxidative stress caused by high blood sugar is the leading reason why pancreatic β-cells die or malfunction. There are several studies that show that diabetic patients have high levels of oxidative stress often associated with hyperglycemia and glucose toxicity.
Astaxanthin’s antioxidant properties can help protect pancreatic beta cells by reducing oxidative stress and sugar toxicity in the blood. In fact, in one milestone study published in 2002, scientists found that astaxanthin reduced glucose toxicity in diabetic mice and therefore protected their pancreatic beta cells.
Astaxanthin can also help patients manage diabetes. In a 2018 study, researchers discovered that astaxanthin can help lower high blood pressure and improve the metabolism of sugar in patients with type 2 diabetes.
As an antioxidant, astaxanthin has countless benefits towards the regaining of the lymph cell dysfunction as well as enhancement of insulin sensitivity, according to another study published in 2006.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today.


There is a growing number of research and studies that seem to suggest that astaxanthin can play a role in keeping your ticker healthy. This is particularly important given that cardiovascular conditions are the leading causes of death worldwide.
For example, a heart attack happens every 40 seconds in the US alone, with heart disease causing over 630,000 American deaths each year.
That’s why it comes as a huge sigh of relief to know that astaxanthin can help prevent or reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. How so?
It helps curb bad cholesterol. High LDL (bad cholesterol) and low HDL (good cholesterol) in the body is a bad combination and risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
In a 2011 blind study, researchers noted that astaxanthin can help reduce the levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) in obese and overweight participants after 12 weeks of use. They also saw a significant reduction in oxidative stress levels.
It regulates blood lipids. Astaxanthin use can also improve the levels adiponectin and HDL, the good cholesterol. A comprehensive study published in 2010 concurs. After 12 weeks of using astaxanthin, subjects with high levels of blood fat experienced a considerable increase in HDL levels.
It enhances blood flow and circulation. A 2006 study involving hypertensive rats (those found to have high blood pressure) revealed that astaxanthin can help improve the thickness and elasticity of the walls of arteries. The Eureka idea here is that the compound can help regulate blood pressure and strengthen arterial walls to prevent heart failure due to hypertension.
It reduces oxidative stress in blood. Another 2000 study examined blood profile of 24 participants after 14-day use of astaxanthin. Results seem to indicate that the supplement can reduce blood oxidation and delays blood clotting.

Nearly half of US adults are hypertensive, but the vast majority are not aware of it. That’s quite unfortunate given there are numerous high-quality heart rate monitors which can help you keep a tab on your blood pressure.
Check out this comparative review of the best heart monitors we published previously and how to pick the right one for you. If you want to stay on top of every aspect of fitness and health, you can never go wrong with a state-of-the-art wrist worn monitor like HeartGuide by Omron.
The best of CES 2019, HeartGuide can take your blood pressure on the go, count your steps, track your fitness, and monitor your sleep — all at the same time!
If you’re a hand-off-ish kind of a person, there are several voice-enabled heart monitors on the market, including Livongo which was recently unveiled at SIGNUM 2019.
That being said, the problem with hypertension often boils down to the resistance to blood flow in the vessels – namely, the arteries, capillaries, and veins.
The narrower your blood vessels (read: blocked arteries due to high LDL cholesterol or triglycerides), the higher your blood pressure. Untreated hypertension can become an increased risk factor for obesity, heart disease, and even stroke.
Astaxanthin has shown great potential in preventing and reducing high blood pressure as well as ameliorating associated effects. And there are several studies that seem to agree.
High cholesterol in the blood can clog your arteries up, which then leads to a buildup in the blood pressure. As we’ve stated above, astaxanthin as an antioxidant helps reduce bad cholesterol and therefore prevent hypertension.
Astaxanthin also fights hypertension by reducing blood oxidative stress and relaxing the walls of the blood vessels. In a study published in 2005 in the Journal of Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, scientists found that astaxanthin use helps regulate nitric oxide (a sign of oxidative stress) and increases the reactivity of blood vessels.
In practice, hypertension can be reduced by losing excess weight, increasing physical activity, limiting alcohol intake, and embracing a healthy diet. It’s all about changing your lifestyle.
When coupled with these activities, astaxanthin can be more effective at reducing high blood pressure.

High cholesterol is a dire condition that is typified by too much low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in the blood. Close to 34 percent of adult Americans are considered to have high LDL cholesterol.
Cholesterol in and of itself isn’t bad. It is produced naturally by the liver and is transported via the blood to be used to make cell membranes, vitamin D and some hormones.
The trouble begins when there’s too much of it in the blood. Because it’s not water-soluble, excess cholesterol usually ends up being deposited on the walls of the blood vessels, specifically on your arteries. That’s never good news because narrow arteries are a perfect recipe for stroke or heart attack.
Traditionally, doctors recommend quitting smoking, eating healthy, exercising and weight loss to people with high cholesterol. Supplementing your diet with astaxanthin has also shown results when it comes to reducing high LDL levels.
One eye-opening study seems to suggest that taking between 6mg and 18mg of astaxanthin every day for 84 days reduces the blood levels of lipids often associated with high LDL levels in individuals with high cholesterol. Not just that — the study also indicated that astaxanthin helps increase the levels of good cholesterol.
Another 2017 research study showed that taking a combination of lycopene, astaxanthin, and other carotenoids for 45 days reduces the levels of triglycerides and LDL cholesterol in male rats.

In the US, it’s estimated that close to 400,000 cases of heart attacks happen outside a hospital environment every year, while another 200,000 cases occur within the confines of a medical facility. As you might already know, some people do survive a heart attack, but they don’t always come out of it unscathed.
What happens in the aftermath of a heart attack can have a huge impact on the quality of life, life expectancy, and chances of repeat cardiac arrest.
That’s where astaxanthin can come in to the rescue.
Specifically, astaxanthin use has been discovered to prevent heart damage not only during an attack but also in the aftermath. In a 2004 study involving dog, rabbit and rat heart attack models, scientists found that there was a reduction in the damage of heart cells in animals pre-treated with astaxanthin.
Although extensive research has not been conducted on human subjects, scientists believe these results can be replicated in humans.
Astaxanthin can also help restore the subtle balance between nitric oxide and peroxynitrite. A nitric oxide/peroxynitrite imbalance is often considered the leading cause of abnormalities in the endothelium, which is the lining of arteries and other blood vessels.
Major complications in the endothelium have been associated with serious health issues, including diabetes, hypertension, poor immune system, insulin resistance, cancer, and atherosclerosis. Changes to the endothelium can also increase damage to the heart in case of a heart attack.
By reducing oxidative stress in the blood, astaxanthin help protect endothelium and therefore “reverse” or prevent extensive heart damage. In fact, in one study published in 2017 in the International Journal of Nanomedicine, scientists found that astaxanthin can help repair cardiovascular damage.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today.


The immune system is much akin to the police for your body. It’s your first and perhaps the last line of defense against viruses, bacteria, and other intruders. If your immune system cannot respond in time, diseases can easily enter your body and cause insurmountable damage to your health.
That’s why an immune response is of paramount importance. Unfortunately, many things can interfere with your normal immune response, including conditions like HIV as well as prolonged inflammation.
Oxidative stress caused by too many free radicals in the body can have adverse effects on the immune response. As a robust antioxidant, astaxanthin can naturally reduce oxidative stress and ensure that your immune system is functioning at an optimal state.
In a 2010 human study, a team of researchers from La Haye Labs, Inc., Inha University in Korea, and Washington State University studied 42 healthy women using astaxanthin for a period of 8 weeks. They found that those who used astaxanthin showed signs of decreased DNA damage and improvement in the immune response.
In another study published in 2015, researchers examined the effects of astaxanthin on lymphatic function via both test-tube study and mice study. They noted that the presence of astaxanthin encouraged the lymphatic glands to produce more lymphocytes which then stimulated the immune response.


Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today!
While stomach ulcers are the most common in the US, there are many known types of ulcers, including genital ulcers, mouth ulcers, venous ulcers, and arterial ulcers.
Peptic ulcers are depicted by a burning sensation in the stomach. This may be accompanied by vomiting, heartburn, bloating, chest pain, nausea, incessant belching, and even sudden drop in weight.
The most common cause of this type of ulcers is infection by the bacteria H. pylori. Your physician and prescribe a concoction of antibiotics to clear the bacterial colony, allowing the ulcers to heal.
Unfortunately, oxidative stress in the gut often creates a conducive environment that allows H. pylori to thrive. That means your stomach ulcers will come back many times until you take care of the oxidative stress.
As mentioned earlier, astaxanthin is a strong antioxidant that reduces oxidative stress. When you take astaxanthin orally, it will help keep H. pylori at bay for good. This helps protect the lining wall of your intestines and prevent ulcer formation.
In one study carried out in 2012, researchers pretreated mice with astaxanthin before inducing gastric ulcers. The mice displayed a significant decline in gastric ulcers when the astaxanthin was used to fight against possible ulcer formation. It also reduced the number of H. pylori – a bacteria behind stomach ulcers.


Antioxidative properties of astaxanthin are also great for your skin. When applied topically, the phytochemical also promotes young-looking, healthy skin.
As you might already know, exposure to UV sun rays can be quite harmful to your skin. Typically, UVA and UVB damage can be reduced using collagen regurgitation and skin thickening regimens. This helps against UV-induced skin damage and photoaging process (the skin signs that we often associate with the aging process).
More importantly, a comprehensive study conducted in 2012 confirmed that combining oral and topical use of astaxanthin can play a big role in reducing age spots, smoothing wrinkles and helping restore skin moisture.
Even better, this anti-aging and skin-promoting results were seen in both female and male subjects. Of course, more conclusive and further studies need to be done to establish the relationship between improved skin health and astaxanthin use.
What’s more exciting are the findings of another 2013 study. This particular study indicated that astaxanthin can not only boost the appearance and health of the skin but can also inhibit the onset of skin cancer.


The list goes on and on. They are all happen when oxidative stress inhibits or reduces the immune response in a particular area of your body. The consequences of bacterial inflammation can be dire. Some recurring infections can also develop resistances antibiotics.
That’s not to mention that certain antibiotics used to treat these infections can have far-reaching side effects. That’s why more and more people are turning to astaxanthin as a natural and safer alternative.
The anti-inflammatory properties of astaxanthin are owed to is antioxidant tendencies. In a study published in the Journal of Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, researchers found that astaxanthin is effective against oxidative stress caused by nitric oxide.
It is this reduced inflammation properties found in astaxanthin that helps protect your lungs, eyes, stomach lining, and heart against bacterial inflammation.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today!
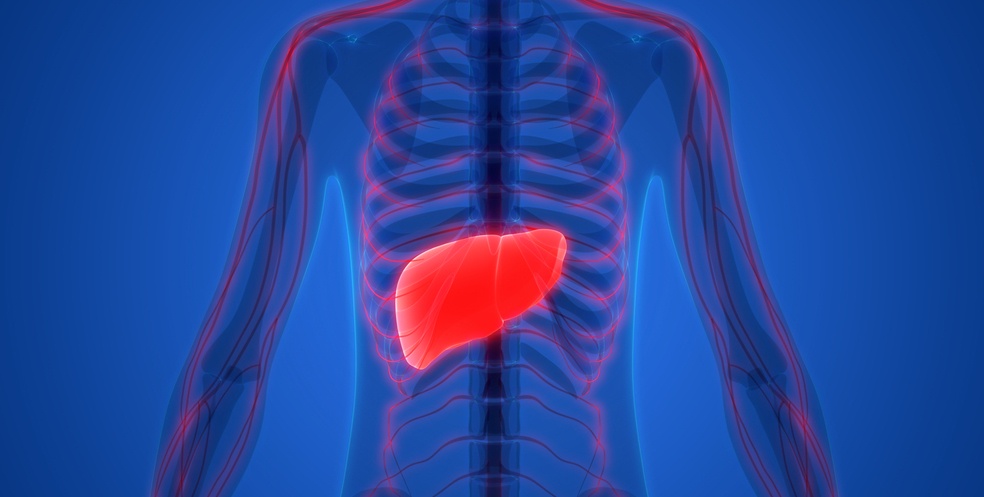

Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NFLD) is one of the two most common types of liver conditions. Both cause significant liver damage, which, in turn, is a BIG risk factor for adverse conditions like cancer, kidney disease, and heart disease.
Fatty liver disease occurs largely due to oxidative stress caused by prolonged inflammation in the liver. It is often associated with metabolic disorders like obesity and accumulation of lipids at the cellular level.
There are two key ways that astaxanthin is known to help prevent or treat fatty liver disease. First, it acts as an antioxidant which stays on top of oxidative stress in the liver. By getting rid of excess radicals caused by metabolic disorders, astaxanthin helps restore normal liver function and avoid liver damage.
It can also work independently of its antioxidant properties to protect the health of the liver. In a 2016 study, Jui-Tung Chen and his team at the Jichi Medical University in Japan found that astaxanthin use can help protect the liver function and prevent fatty liver disease, cancerous disease, and cardiovascular disease.
Another study published recently in 2018, scientists discovered that astaxanthin is effective against alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice by their regulating gut bacteria. There’s no shortage of studies targeting the astaxanthin efficacy when it comes to treating liver disease.

In one early study, scientists discovered that astaxanthin has both short-term and long-term benefits as far as treating breast cancer is concerned. More specifically, they found that the antioxidant helps tame the growth of cancerous breast cells.
Unfortunately, the exorbitant cost associated with purifying astaxanthin has limited its use in cancer treatment.
An even earlier study published in 1995 involved the use of astaxanthin to treat cancer in mice. The findings were quite interesting. 32-week use of astaxanthin showed significant inhibition of tumor formation and growth in mice and rats with chemically-induced cancers.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today!


The fact that astaxanthin gives salmon its bright reddish color speaks volumes about the effectiveness of the antioxidant when it comes to boosting physical performance.
Heavy workouts and demanding exercises like swimming, running and weight lifting often lead to the accumulation of stress hormone cortisol as well as increased release of metabolic free radicals. This is a surefire recipe for oxidative stress which can cause fatigue, tiredness, and sore muscles during and after the exercise.
The good news is that there’s been a barrage of studies on how astaxanthin might help increase endurance, boost physical stamina and reduce fatigue levels during and after intensive exercises. The preliminary findings and results have been commendable.
First off, several studies on lab rats and mice have shown that astaxanthin can help encourage the body to use its own reserve of fats. This not only helps boost your endurance but also reduces the risk of skeletal and muscle damage. The last finding is corroborated by another mice study published in 2004.
Although extensive research needs to be done to establish these health claims, a few human studies have been fairly positive. Take this 2005 study, for instance. Scientists found that astaxanthin supplementation may not reduce the likelihood of injury but can help spruce up endurance and stamina.
Of course, there are several ways you can reduce exercise fatigue which can be used in combination with astaxanthin. These include the use of protein coffee, regular hydration, getting plenty of sleep, and taking iron-rich foods.

It is thought that an American adult has a stroke every 40 seconds. Like heart attack which causes heart damage, stroke can have adverse damage on the brain tissue, CNS (central nervous system), cranial membranes and cells.
Only 20 percent of stroke cases are not preventable. Even still, stroke can damage many vessels that supply blood to several regions of the brain. By denying oxygen and vital nutrients, the brain cells usually die.
Astaxanthin can play a key role in preventing and reducing brain damage from stroke. It works by stimulating blood flow, reducing blood pressure, relaxing blood vessels, and ameliorating oxidative stress.
In one interesting study published in 2010, researchers found that giving rats or mice high dosage of astaxanthin can help reduce stroke-related brain damage. The research also showed a significant reduction in brain damage from a stroke.
The study also showed that astaxanthin supplementation reduces neurotoxicity caused by nitric oxidation.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today.

Brain injury can have a devastating effect on the victim’s neurological functions and can deal a blow to their quality of life. Brain injury can result from serious fall/slips, sports-related accidents, traffic accidents, physical assaults, and major trauma.
Whatever the cause, recovery from a head injury can be difficult, especially if it is extensive. Astaxanthin seems to help accelerate recovery from particularly traumatic forms of brain injury (TBI), according to a 2017 study. Other studies have shown that while it can speed up the recovery, astaxanthin may have little to no impact on cognitive function.
On a more positive note, using astaxanthin to treat brain injury has shown to help reduce swelling from injuries and promoting slight key brain function. As such, it may be prudent to include astaxanthin in your diet to promote faster resurgence from a brain injury.
Remember a traumatic brain can last a lifetime to recover, so any bit of boost is often a welcome reprieve. The recovering patient may have to take the antioxidant on a daily or regular basis to reap the most recovery benefits and accelerate the return of normal cognitive function.


Did you know that 4 out of every 5 cases of dementia are due to Alzheimer’s?
There is no known cure for this chronic ongoing condition at the moment. However, there are several psychotherapies, medications and other treatment options that can help reduce Alzheimer’s disease progression, improve quality of life and mitigate the symptoms.
As an antioxidant, astaxanthin has joined the list of potential treatment options for Alzheimer’s. There is a multitude of ongoing studies on the effects of astaxanthin for Alzheimer’s, but preliminary results are something to write home about.
For example, in a 2010 study, scientists were thrilled to discover that antioxidant properties of astaxanthin can be instrumental in reducing the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, especially the early onset type.
While the condition cannot be treated fully, protecting those at higher risk for the disease is very crucial.
When combined with lifestyle changes, studies have shown that astaxanthin can be effective at preventing and decelerating the progression of Alzheimer’s.
That’s groundbreaking because the substance can help reduce neurodegeneration and recover some of the neurological functions.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today!


Increased oxidative stress in the brain has been found to be responsible for many neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, and much more.
Like Alzheimer’s, Parkison’s disease is a progressive neurological ailment that’s also characterized by severe loss of memory (dementia). It is a life-changing disorder with over 50,000 new cases reported in the US annually. It is typified by loss of coordination, motion, and neurological function.
It’s deemed the 14th leading cause of death in America, according to the Center for Disease Control (CDC). Like its cousin, the Alzheimer’s disease, there is currently no cure for Parkinson’s disease.
However, there have been protective effects seen in the disease when treated with astaxanthin, which might potentially prevent or slow down the development of symptoms.
Experts believe that the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of astaxanthin play a role in the protection of mitochondria and nerve cells. In saying that, they seem to suggest that the antioxidant is a potential treatment for Parkinson’s.


For instance, in a 2011 study, Parviz Gharagozloo and his research colleagues at the Priority Research Centre in Reproductive Science of the University of Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia found a strong link between high levels of sperm oxidative stress and male infertility.
As such, fertility experts and scientists have been actively studying how to use antioxidants to deal with sperm oxidative stress and therefore cure male infertility. It turns out, astaxanthin is literally what the doctor prescribed!
One intriguing study published in 2005 shows positive results of astaxanthin for treating infertility in men. In a 3-month period, the researchers assessed 30 individuals diagnosed with male infertility. In the course of the study period, scientists noted uptick and positive improvements in several sperm metrics.
The first positive results in men treated with astaxanthin included reduced death of sperm, increased the count and an overall improvement in vitality and fertility. The small size of the study group warranted further and more extensive research to establish for sure that the antioxidant can help with male infertility.
Accordingly, another 2013 study showed that astaxanthin can help improve “human sperm capacitation.” There are also several ongoing treatment trials for infertility in men using astaxanthin.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today!


As per early research conducted by scientists, a combo supplement comprising astaxanthin has been found to help reduce these menopause symptoms. These are especially climacteric symptoms like hot flushes that are often associated with high levels of cortisol (a stress hormone) and oxidative stress.
In one particular study published in 2017 and another one conducted in 2018, researchers found this to be true. Not only does astaxanthin help with skin care, heart repair, and exercise fatigue, it can also prevent signs associated with menopause.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today!

From preliminary examinations, there seems to be a future of astaxanthin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Of course, there are multiple alternative treatments, including the use of CBD oil. Or companies like Principia or Horizon Pharma developing drugs to tackle this condition.
As a far as astaxanthin is concerned, the results are positive yet mostly inconclusive. Packed with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, it is not surprising that researchers exploring if astaxanthin can help reduce pain symptoms and inflammation related to rheumatoid arthritis.
Take, for instance, this study that was published in 2012 in the publication of the American Association for Hand Surgery. The relationship may be inclusive, but one thing is clear: astaxanthin is a promising option for managing rheumatoid arthritis.
Buy Astaxanthin on Amazon.com today!
Astaxanthin is currently one of the most talked-about carotenoids, a class of reddish-pink pigments found naturally in algae, and in salmon, crabs, shrimp, lobster, and other seafood. It’s also what gives the feathers of flamingo that beautiful pink coloration.
Carotenoids have a colorful and fascinating history, having been researched since the early 1800s. Astaxanthin belongs to the Xanthophylls subgroup of carotenoids, with the famous carotenes like lycopene, alpha-carotene, and beta-carotene being the other subclass.
Astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant, which is the overarching property behind its several health benefits. What that means is that it naturally reduces oxidation, a biological process that helps keep many health issues and conditions at bay.
Oxidative stress is a condition that arises when the balance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body tips towards the former. Too many radicals are responsible for many cases of inflammation in the body.
Astaxanthin can help curb oxidative stress in several parts of the body by neutralizing free radicals. This is the holy grail in the manner in which antioxidants help prevent disease.
By the same token, astaxanthin might play a key role in many body changes and disease. These include:
Cancer treatment. Owing to its antioxidant properties, a growing number of studies have shown that astaxanthin may help treat several cancers, most notably breast cancer, prostate cancer, and leukemia. Further research is still needed, though.
Skin care and UV protection. A handful of studies have revealed that the antioxidant can slow down the photoaging process and prevent UV-induced cancer damage.
Ulcers. Astaxanthin help control ulcer-causing bacteria, H. pylori. By doing so, it allows ulcer wounds to heal faster and prevent a recurrence.
Heart disease prevention. Astaxanthin plays a role in reducing high cholesterol, increasing blood flow, and relaxing blood vessels. The combination of the three positive effects results in a healthy heart.
On a similar note, astaxanthin helps with heart damage repair. It prevents unwanted changes to the endothelium, protecting the walls and arteries in the heart. It also allows damaged heart cells to regenerate.
It helps curb oxidative stress in the brain. This plays an important role in treating and managing brain-related and neurodegenerative disorders including traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Treating male infertility. Increased sperm oxidative stress has been associated with low fertility or infertility in men. As an antioxidant, astaxanthin helps nib this in the bud.
Helps with exercise-related fatigue. Astaxanthin encourages the body to take advantage of its own supply of fatty lipids, which improves exercise endurance, stamina, and muscle fatigue during and after exercising.
Reduces high cholesterol. Its action on oxidative stress in the blood can help reduce high blood pressure, improve heart health, prevent diabetes, and decrease the risk of brain damage from stroke.
It’s a powerful anti-inflammatory agent. Astaxanthin has been found to possess plenty of anti-inflammatory properties.
This may come in handy as a treatment option for conditions and diseases that involve inflammation, including bacterial inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, several types of cancer, and carpal tunnel syndrome, just to mention a few.
While further and more conclusive research has to be conducted to establish firmly these health benefits and claims, you can rest assure that astaxanthin is best for you by virtue of being an antioxidant.
To reap the full health benefits of astaxanthin, you might want to load up on foods rich in the antioxidant at least two times a week. Alternatively, you can take astaxanthin supplements from a reputable seller.